Atherosclerosis Is Characterized by the Deposition of Lipids in the:
Atherosclerosis is the result of hyperlipidemia and lipid oxidation and has always been a major cause of mortality in developed countries. This deposition can cause sudden death by blocking blood supply to the heart.
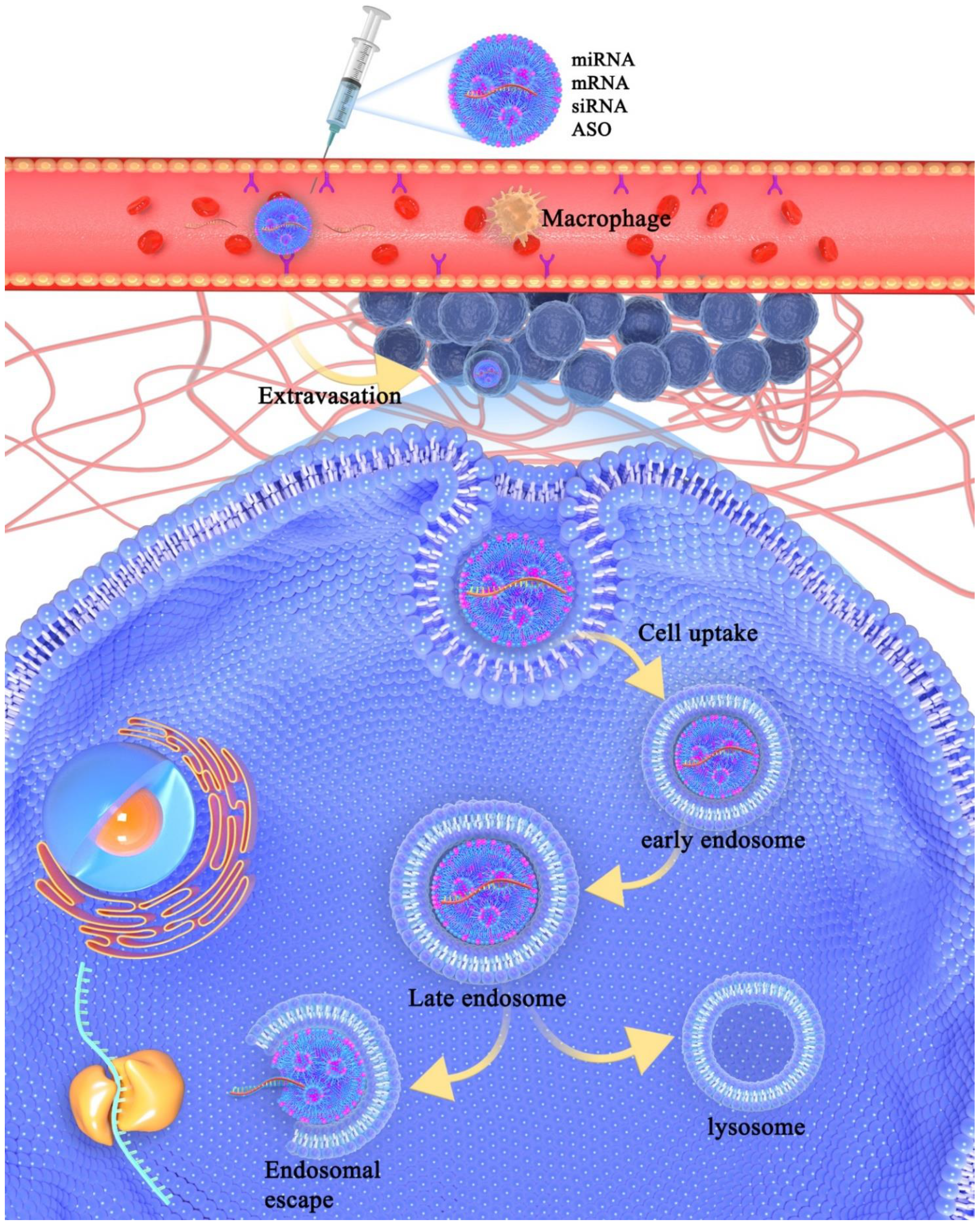
Molecules Free Full Text Modification Of Lipid Based Nanoparticles An Efficient Delivery System For Nucleic Acid Based Immunotherapy Html
Plaque rupture and the consequent thrombosis may.

. The butterfat diet produced severe aortic lesions characterized by abundant lipid deposition and relatively little cell proliferation or collagen deposition. Atherosclerosis is characterized as a chronic inflammatory disease of the vessel wall and is typified by an accumulation of lipids in arterial walls the infiltration of. ˌæθərəʊsklɪəˈrəʊsɪs n pl -ses -siːz Pathology a degenerative disease of the arteries characterized by patchy thickening of the inner lining of the arterial walls caused by deposits of fatty material.
Atherosclerosis is characterized by patchy intimal plaques atheromas that encroach on the lumen of medium-sized and large arteries. Atherosclerosis is a multifactorial disease that affects the intima of elastic arteries. Cell death and inflammation play critical roles at various stages of atherosclerosis.
Risk factors include dyslipidemia diabetes cigarette smoking family history sedentary lifestyle obesity and. The core region of atherosclerotic plaques is characterized by profuse lipid deposition and disappearance of cells and fibrous tissue elements. A form of arteriosclerosis.
The anatomy of a normal artery is shown in Fig. The early lesions of atherosclerosis consist of subendothelial accumulations of cholesterol-engorged macrophages called foam cells. Atherosclerosis is associated with inflammatory processes in the endothelial cells of the vessel wall associated with retained low-density lipoprotein LDL particles.
It is a disease of vascular intima in which all the vascular system from aorta to coronary arteries can be involved and is characterized by intimal plaques 1 2. Individuals with atherosclerosis have a higher risk of coronary artery disease and stroke. Up to 10 cash back Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by the deposition of excess lipids in the arterial intima.
The early stages of atherosclerosis are characterized by the deposition of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides into the arterial wall. Type of arteriosclerosis characterized by thickening and lipid deposition in the tunica intima of arteries inflammatory disease overview of stages of development of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a progressive disease characterized by the accumulation of lipids and fibrous elements in the large arteries.
The formation of macrophage-derived foam cells in a plaque is a hallmark of the development of atherosclerosis. The formation of macrophage-derived foam cells in a plaque is a hallmark of the development of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of death in developed countries and is characterized by the deposition of fibrous tissues and lipids in the intima of elastic arteries leading to thrombus formation and structural damage marked by thickening and hardening of the vessel walls.
Begins with arterial endothelial injury - atheroma lipid cholesterol core develops - arterial blood flow descreases. The plaques contain lipids inflammatory cells smooth muscle cells and connective tissue. The formation of macrophage-derived foam cells in a plaque is a hallmark of the development of atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is an important cause of cardiovascular diseases such as ischemic heart disease and stroke. 25 26 This retention may be a cause an effect or both of the underlying inflammatory process. This complex multifactorial disease has chronic and progressive pathology characterized by lipid accumulation low-grade inflammation in the walls of large- and medium-sized arteries and endothelial dysfunction 1 2.
Lipid homeostasis especially cholesterol homeostasis plays a crucial role during the formation of foam cells. Atherosclerosis is a progressive disease characterized by the accumulation of lipids and fibrous elements in the large arteries. Lipid homeostasis especially cholesterol homeostasis plays a crucial role during the.
The disease is characterized by intramural deposits of lipids proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts and accumulation of macrophages. Lipid homeostasis especially cho-lesterol homeostasis plays a crucial role during the formation of foam cells. Atherosclerosis is characterized by the deposition of excess lipids in the lumen of major blood vessels.
Fatty streaks form from the deposition of lipid including cholesterol esters in macrophage and smooth muscle resulting in foam cells. This early stage is thought to be reversible. In the excised human atherosclerotic plaque these lipids are in a liquid-like state at body temperature and observable via MRI and NMR spectroscopy.
A form of arteriosclerosis characterized by the deposition of atheromatous plaques containing cholesterol and lipids on the innermost. Gross examination of the arteries revealed a definite difference in the degree and the characteristics of aortic atherosclerosis among the three dietary groups. Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by the deposition of excess lipids in the arterial intima.
Form of arteriosclerosis characterized by the deposition of atheromatous plaques containing cholesterol and lipids on the innermost layer of the walls of large and mediumsized arteriesThe condition in which an artery wall thickens as the result of a build-up of fatty materials such as cholesterolHardening of the arteriesA form of arteriosclerosis in which fatty deposits. Enlargement of the core unless impeded or contained leads to plaque rupture and. Atherosclerosis is characterized by vascular obstruction from the deposits of plaque resulting in reduced blood flow.
A form of arteriosclerosis characterized by the deposition of plaques containing cholesterol and lipids on the innermost layer of the walls of large- and medium-sized arteries. The second stage involves extracellular deposition of plaques which also contain cholesterol esters as well as dermatin sulfate and platelets. Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by the deposition of excess lipids in the arterial intima.
Atherosclerosis is the leading cause of death in North America and within the next two decades will be the leading cause worldwide.

Accumulation Of Plasma Derived Lipids In The Lipid Core And Necrotic Core Of Human Atheroma Imaging Mass Spectrometry And Histopathological Analyses Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis And Vascular Biology

The Role Of Lipids And Lipoproteins In Atherosclerosis Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

Lipid Ingestion And Metabolism Lipids From Foods Are Digested In Gi Download Scientific Diagram
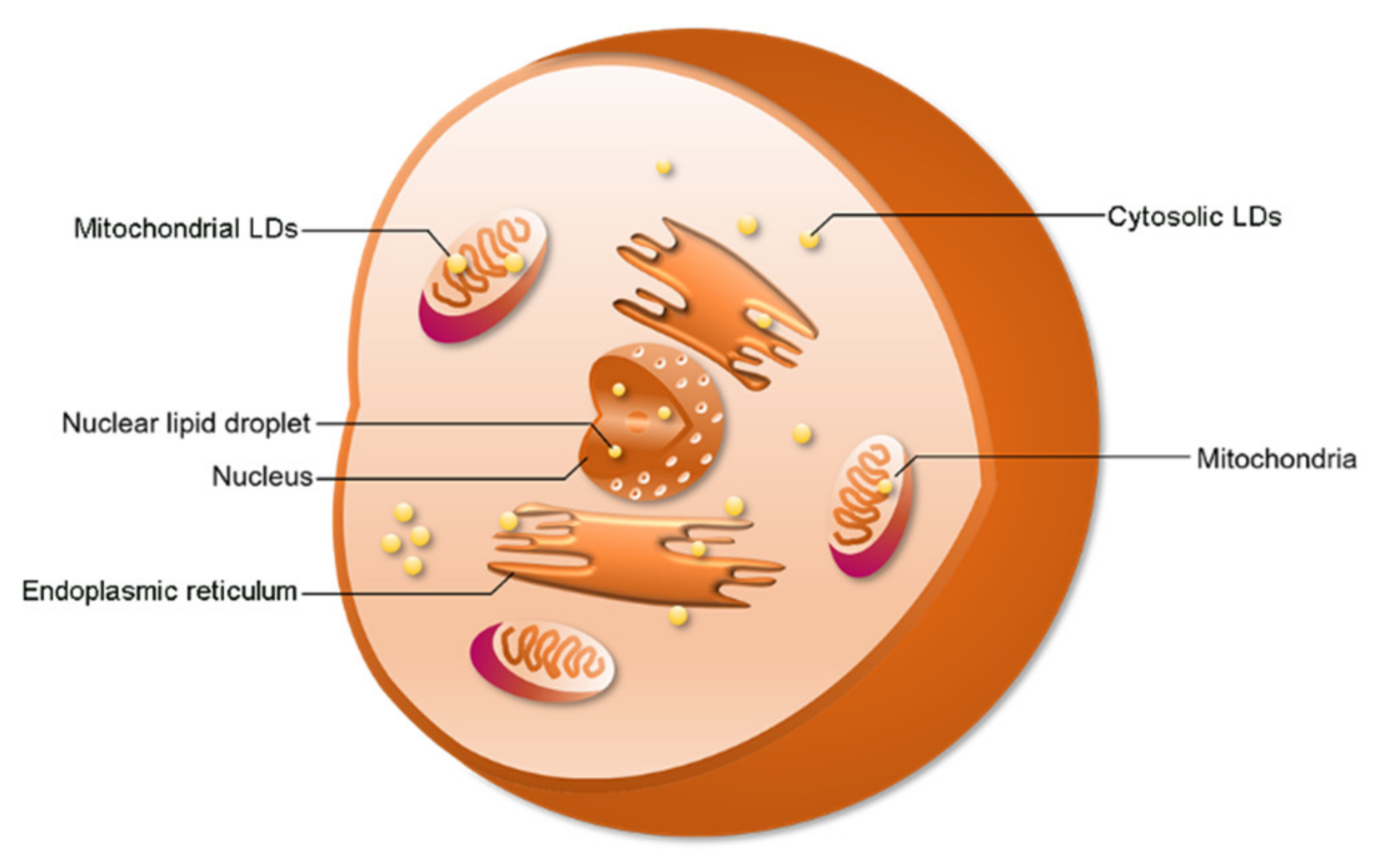
Ijms Free Full Text Seipin A Key Factor For Nuclear Lipid Droplet Generation And Lipid Homeostasis Html

Mechanisms Of Lipid Handling In Macrophages Endothelial Cells Have A Download Scientific Diagram
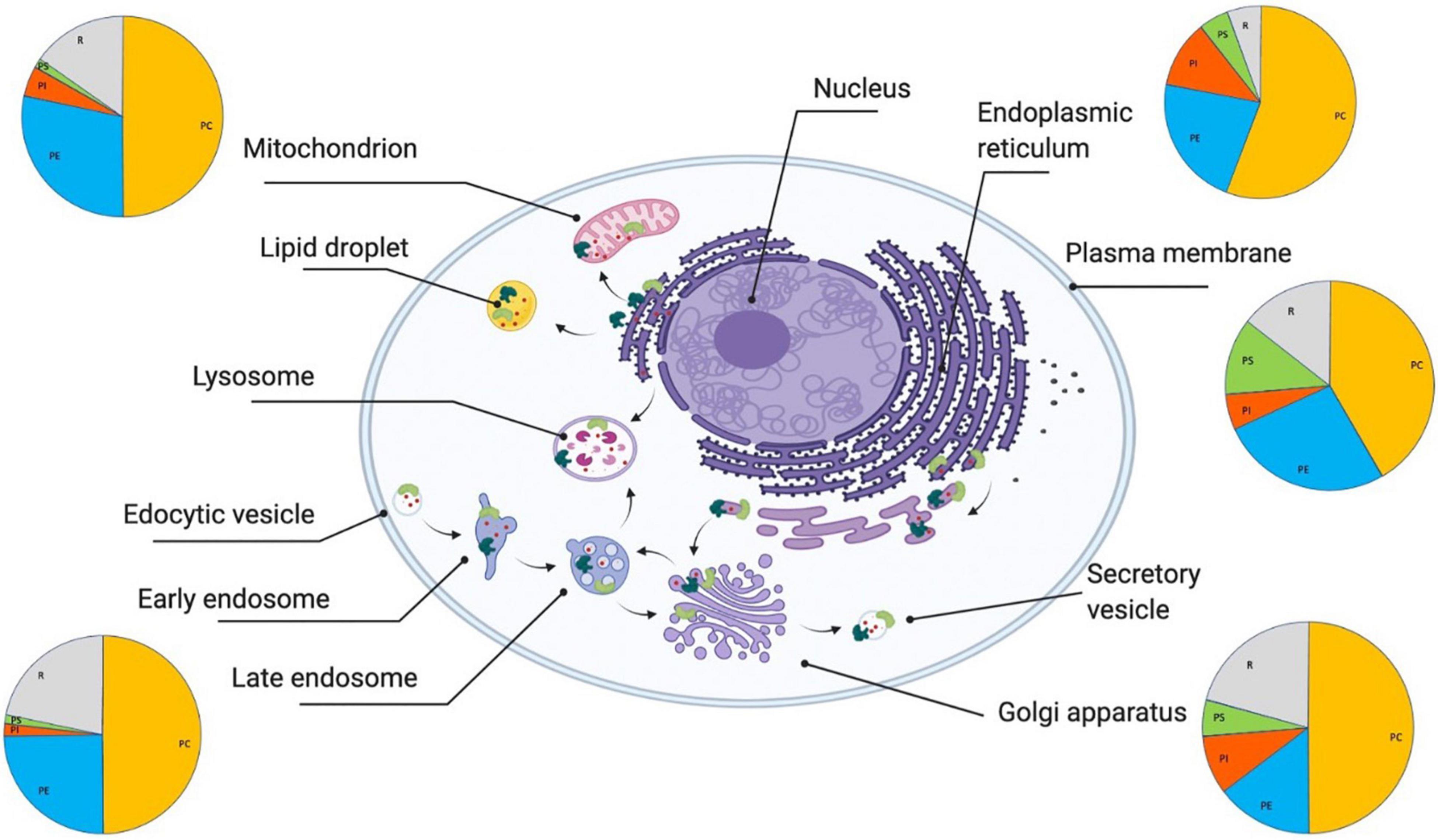
Frontiers Lipid Homeostasis And Its Links With Protein Misfolding Diseases Molecular Neuroscience

Pdf Ldl Mimetic Lipid Nanoparticles Prepared By Surface Kat Ligation For In Vivo Mri Of Atherosclerosis

The Role Of Lipids And Lipoproteins In Atherosclerosis Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

Lipid Metabolism Overview Animation Youtube

Atherosclerosis Pathology Britannica
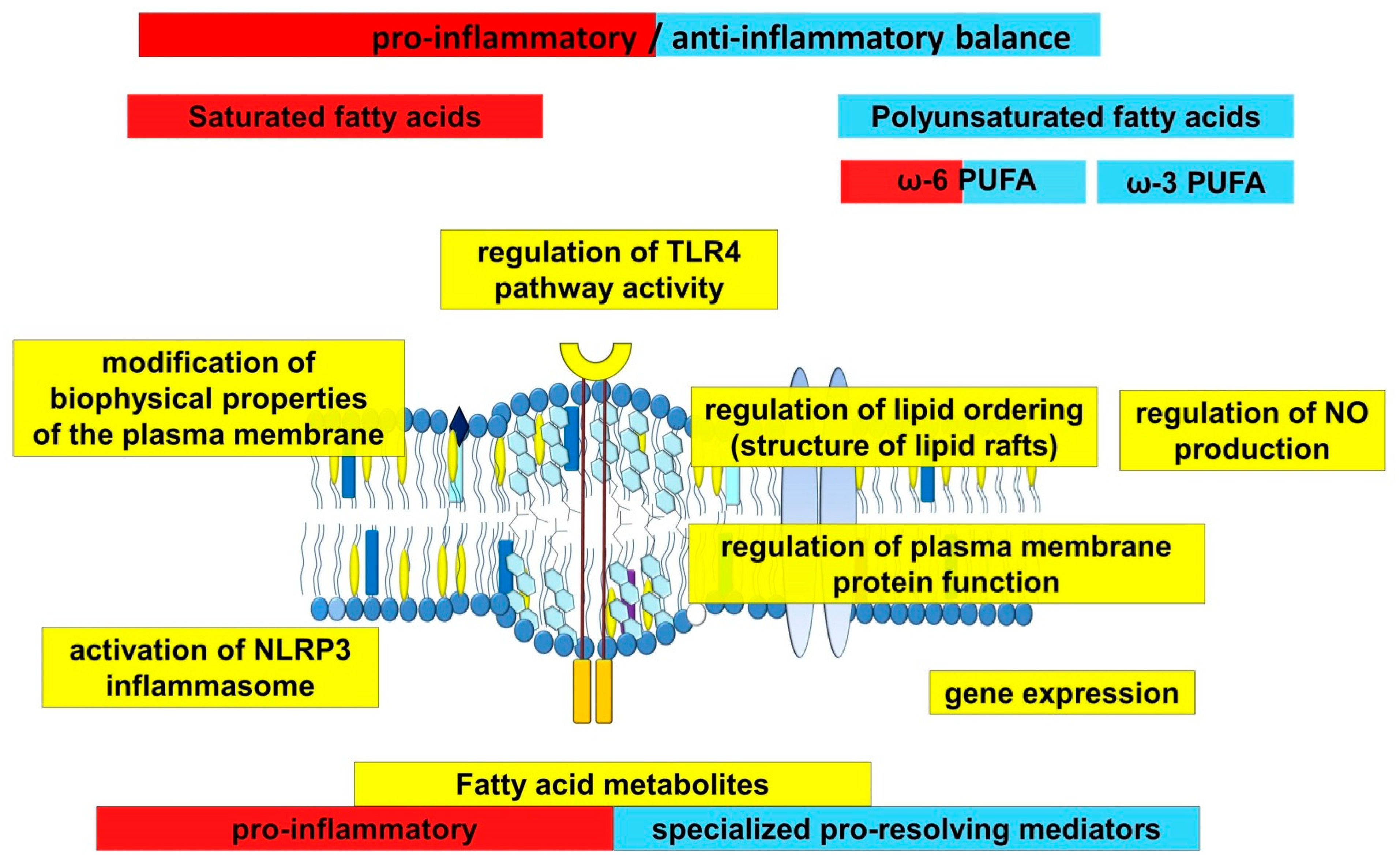
Ijms Free Full Text Involvement Of Fatty Acids And Their Metabolites In The Development Of Inflammation In Atherosclerosis Html
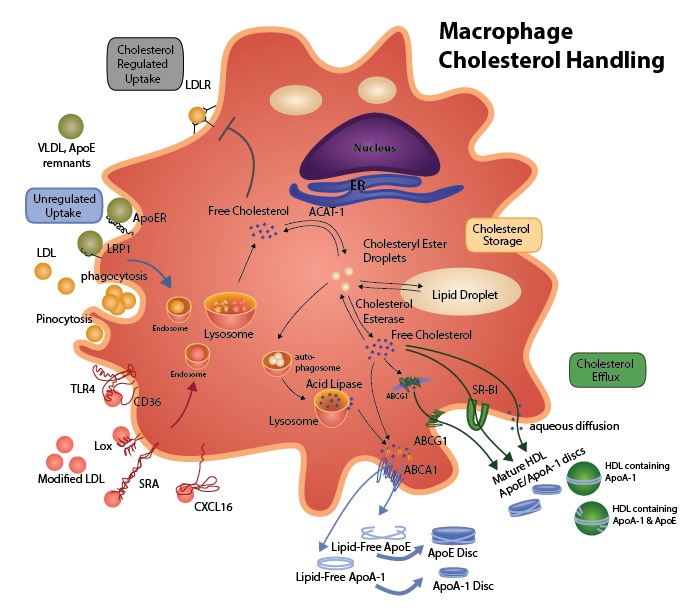
The Role Of Lipids And Lipoproteins In Atherosclerosis Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

295 Triglyceride Illustrations Clip Art Istock
Overview Of Ischemic Heart Disease Calgary Guide
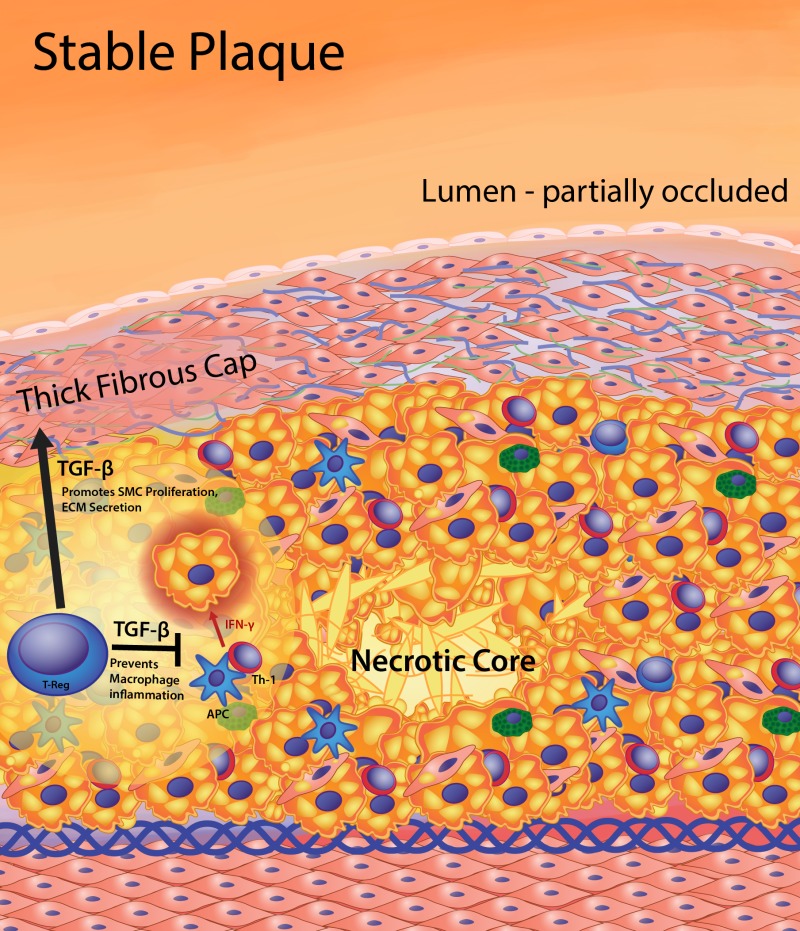
The Role Of Lipids And Lipoproteins In Atherosclerosis Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

Lipoprotein A As A Cause Of Cardiovascular Disease Insights From Epidemiology Genetics And Biology Journal Of Lipid Research

Roles Of Macrophages In Different Stages Of Atherosclerosis Download Scientific Diagram

Effects Of Bariatric Surgery On Lipid Lipoprotein Profile Metabolism Clinical And Experimental

Overview Of Ischemic Heart Disease Calgary Guide Ischemic Heart Disease Coronary Artery Disease Disease
Comments
Post a Comment